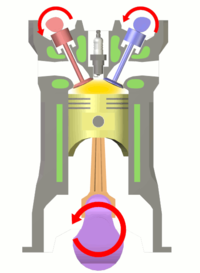
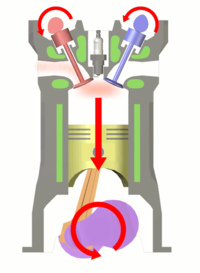
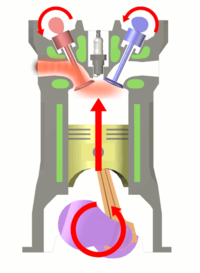
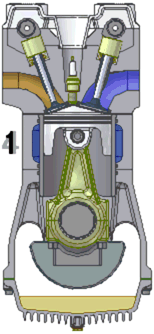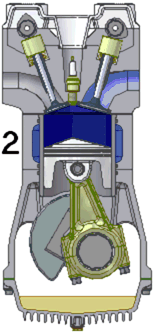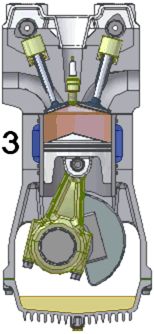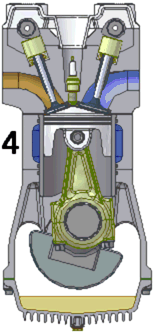
The two-stroke internal combustion engine differs from the more common four-stroke engine by completing the same (thermodynamic) cycle in only two strokes of the piston, rather than four. This is accomplished by using the beginning of the compression stroke and the end of the combustion stroke to simultaneously perform the intake and exhaust functions, which is called scavenging. This allows a power stroke for every revolution of the crank, instead of every second revolution as in a four-stroke engine. For this reason, two-stroke engines provide high specific power, so they are valued for use in portable, lightweight applications such as chainsaws as well as large-scale industrial applications like locomotives.

Invention of the two-stroke cycle is attributed to Dugald Clerk around 1880 whose engines had a separate charging cylinder. The crankcase-scavenged engine, employing the area below the piston as a charging pump, is generally credited to Joseph Day (and Frederick Cock for the piston-controlled inlet port).